The Relationship Between the Implementation of the Implementation of the Demonstration Method and Student Learning Motivation in Fiqh Subject at Said Yusuf Islamic Junior High School Depok
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69526/bir.v3i3.350Keywords:
Demonstration Method, Learning Motivation, FiqhAbstract
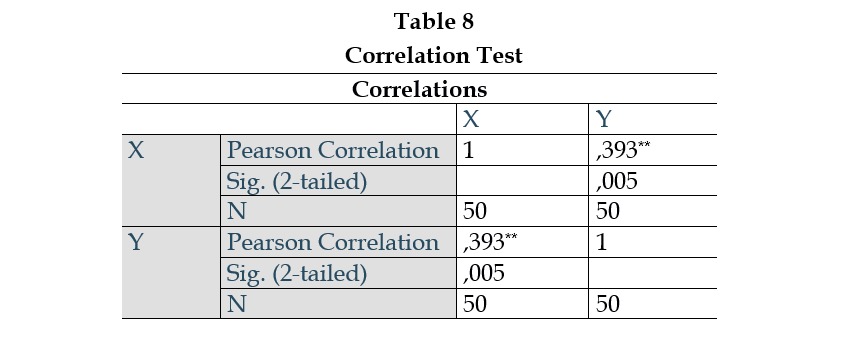
Learning motivation refers to the internal drive within students that encourages them to acquire knowledge to achieve the success they aspire to. The lack of learning motivation in students becomes a challenge because the teacher’s teaching strategies are less innovative, particularly in applying teaching methods. The purpose of this research is to determine the relationship between the Demonstration Method and learning motivation at SMP Islam Said Yusuf Depok. The research variables include the Demonstration Method (X) and Learning Motivation (Y). The population in this study consisted of all students at Sa'id Yusuf Islamic Middle School, totaling 131 individuals. The sampling technique used was purposive sampling, so the sample taken specifically for class VIII students amounted to 50 people. Data was collected through observation, interviews, questionnaires, and documents. Data analysis was performed using SPSS statistics, including data description, validity test, reliability test, normality test, linearity test, and correlation test with product-moment Pearson correlation, significance test, and coefficient of determination. The data description for the Demonstration Method shows an average score of 125.62, a median of 127.50, a mode of 130, a standard deviation of 8.647, and a variance of 74.771, with the highest score being 147 and the lowest being 106. The data description for learning motivation shows an average score of 116.96, a median of 118.00, a mode of 102, a standard deviation of 8.647, and a variance of 329.546, with the highest score being 148 and the lowest being 78. The hypothesis test results, which examine the relationship between the Demonstration Method (variable X) and learning motivation (variable Y), show a correlation coefficient of r = 0.393 > r table 0.279. Therefore, Ha is accepted, and Ho is rejected, indicating a positive relationship between the demonstration method and learning motivation in Fiqih subjects at SMP Islam Said Yusuf Depok. The correlation between these variables is statistically significant, as demonstrated by the t-test value of 2.960 > t table 2.021. The coefficient of determination is 0.154, meaning the contribution of the Demonstration Method to learning motivation is 15.4%, with the remaining influence coming from other factors.
References
E. Siti Faridah and Salma Aisyah Amini, “The Influence of Islamic Spiritual Extracurricular Activities on PAI Learning Outcomes of Students at State Senior High School 1 Bojonggede, Bogor Regency,” Bull. Islam. Res., vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 89–106, Jun. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.69526/bir.v1i2.348.
Siskha Putri Sayekti, “Systematic Literature Review: The Role of Islamic Religious Education Teachers in Instilling Religious Moderation in Elementary Schools,” Bull. Islam. Res., vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 107–122, Jun. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.69526/bir.v1i2.343.
F. Arfan, Muhammad Raffa, and Indra Nurhadi, “Bibliometric Analysis of Social Support for Children’s Mental Health in the Perspective of Islamic Education,” Bull. Islam. Res., vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 123–142, Jun. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.69526/bir.v1i2.340.
A. Iman hartafan, “Analysis of Self-Harm Behavior in Islamic Psychology: Trends, Impact, and Future Research Directions through Bibliometric Study,” Bull. Islam. Res., vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 143–162, Jun. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.69526/bir.v1i2.344.
Isninda Nur Masithoh, “Implementation of The Values of Religious Moderation and Morals in Extracurricular Learning of Ratoh Jaroe Dance Cultural Arts,” Bull. Islam. Res., vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 163–176, Jun. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.69526/bir.v1i2.359.
Md. Ishaque, M. Mahmudulhassan, and Muhammad Abuzar, “Sustaining Digital Faith: How Technology Impacts Religious Activities and Participation in the Digital Era,” Bull. Islam. Res., vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 177–188, Jun. 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.69526/bir.v1i2.338.
L. Bainotti, “Qualitative methods,” in Elgar Encyclopedia of Technology and Politics, University of Amsterdam, Netherlands: Edward Elgar Publishing Ltd., 2022, pp. 118–122. doi: https://doi.org/10.4337/9781800374263.qualitative.methods.
A. Cissé and A. Rasmussen, “Qualitative Methods,” in Comprehensive Clinical Psychology, Second Edition, vol. 3, Fordham University, Bronx, NY, United States: Elsevier, 2022, pp. 91–103. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818697-8.00216-8.
V. Eatough and L. Tomkins, “Qualitative methods,” in Language and Emotion: An International Handbook, vol. 1, London, United Kingdom: De Gruyter, 2022, pp. 163–182. doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110347524-008.
C. Alfonso and Á. Antelo, “Quantitative and qualitative methods, primary methods,” in Environmental Toxicology, Plaza Santo Domingo 20-5a, Lugo, 27001, Spain: De Gruyter, 2018, pp. 58–90. doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110442045-003.
C. Alfonso, “Quantitative and qualitative methods, and primary methods,” in Environmental Toxicology: Non-bacterial Toxins, Laboratorio CIFGA S.A., Avenida Benigno Rivera, 56, Lugo, 27003, Spain: De Gruyter, 2024, pp. 65–101. doi: https://doi.org/ 10.1515/9783111014449-003.
W. H. Macey, “Qualitative methods in engagement research,” in A Research Agenda for Employee Engagement in a Changing World of Work, CultureFactors, United States: Edward Elgar Publishing Ltd., 2021, pp. 175–191. doi: https://doi.org/10.4337/9781789907858.00020.
UU RI No. 20, “Undang-undang (UU) Nomor 20 Tahun 2003 tentang Sistem Pendidikan Nasional,” 8 Juli 2003, Jakarta, Jul. 08, 2003.
Lajnah Pentashihan mushaf Al-Qur’an, “Qur’an Kemenag.” Accessed: Mar. 24, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://quran.kemenag.go.id/
H. B. U. B.Uno, Teori Motivasi dan Pengukurannya. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara, 2011.
D. Djaali, Psikologi Pendidikan. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara, 2008.
A. M. Sardiman, Interaksi dan Motivasi Belajar Mengajar. Jakarta: Rajawali Press, 2018.
A. Nata, Perspektif Islam tentang Strategi Pembelajaran. Jakarta: Kencana, 2009.
I. Isjoni, Pembelajaran Visioner Perpaduan Indonesia-Malaysia. Yogjakarta: Pustaka Pelajar, 2007.
A. L. Hakim, “Pengaruh Pendidikan Anak Usia Dini terhadap Prestasi Belajar Siswa Kelas I Sekolah Dasar di Kabupaten dan Kota Tangerang,” 1, vol. 17, no. 1, Art. no. 1, Jan. 2011, doi: https://doi.org/10.24832/jpnk.v17i1.11.
D. P. N. Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, Kamus Besar Bahasa Indonesia Pusat Bahasa. Jakarta: Gramedia Pustaka Utama, 2012.
A. Rahman, Psikologi Suatu Pengantar dalam Perspektif Islam. Jakarta: Kencana, 2008.
S. Bahri, Psikologi Belajar. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta, 2011.
K. Kompri, Motivasi pembelajaran : Perspektif guru dana siswa. Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya, 2016.
S. Bahri, Psikologi Belajar. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta, 2011.
M. Syarif, Strategi Pembelajaran Teori dan Praktik di Tingkat Pendidikan Dasar. Jakarta: Rajawali Pers, 2015.
E. Emzir, Metodologi Penelitian Kualitatif Analisis Data. Jakarta: Rajawali Pers, 2016.
S. Sugiyono, Metode Penelitian Pendidikan Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta, 2016.
S. Arikunto, Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan Praktik. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta, 2014.
S. Azwar, Metode Penelitian Psikologi. Yogjakarta: Pustaka Pelajar, 2014.
S. Sugiyono, Metode Penelitian Pendidikan Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta, 2016.
S. Siregar, Statistik Parametrik untuk penelitian Kuantitatif. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara, 2013.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Eva Siti Faridah, Huliyatul Atqiya (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



















