The Influence of Islamic Spiritual Extracurricular Activities on PAI Learning Outcomes of Students at State Senior High School 1 Bojonggede, Bogor Regency
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69526/bir.v1i2.348Keywords:
Islamic Spiritual Activities, Extracurricular Activities, PAI Learning Outcomes, SPSSAbstract
Abstract
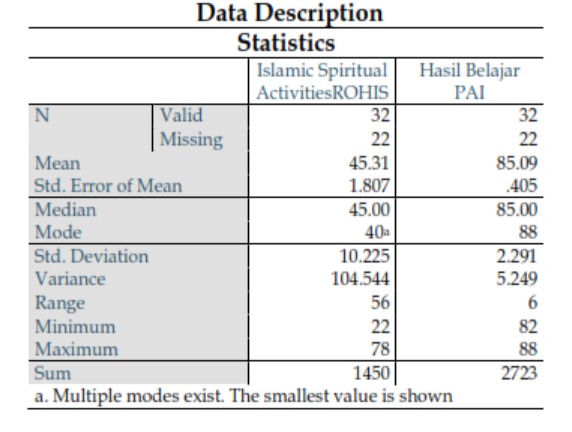
Islamic Spiritual Activities (ROHIS) are highly beneficial in shaping a generation of Muslims who not only impact learning outcomes but also influence their spirituality. This research aims to address the issue of whether ROHIS activities affect the learning outcomes of Islamic Religious Education (PAI). This study uses a Quantitative Method, also known as field research, conducted at SMA Negeri 1 Bojonggede, Bogor Regency. It provides an overview of the issues through analysis with a scientific approach based on the situation in the field. The study aims to examine how the influence of Islamic Spiritual Extracurricular Activities affects the learning outcomes of PAI for 11th-grade students at SMA Negeri 1 Bojonggede. The research data collected were analyzed using SPSS through several tests, including Descriptive Data, Instrument Test, Prerequisite Test, and Hypothesis Test. Based on the descriptive data calculations using descriptive statistics, it was found that the average score for variable X = 45.31 and variable Y = 85.09, the median or middle value for variable X = 45.00 and variable Y = 85.00, the mode or most frequent value for variable X = 40 and variable Y = 88, the standard deviation or difference score for variable X = 10.225 and variable Y = 2.291, the variance for variable X = 104.544 and variable Y = 5.249, the range score for variable X = 56 and variable Y = 6, the minimum score for variable X = 22 and variable Y = 82, the maximum score for variable X = 78 and variable Y = 88, and the total score for variable X = 1450 and variable Y = 2723. To determine whether there is an effect of variable X on Y, a Hypothesis Test was conducted using the Pearson product-moment correlation formula, a Significance Test using the t-test, and a Determination Coefficient. The results of the correlation test showed that the value of rhitung = 0.442 > r table = 0.266, Ha is accepted and Ho is rejected, indicating a positive influence of ROHIS activities on PAI learning outcomes. The results of the significance test show that the p-value (sig.) = 0.011 > 0.05 and the t-count value = 2.700 > t-table = 1.674, so Ha is accepted and Ho is rejected, indicating a significant correlation between ROHIS activities and PAI learning outcomes. The contribution calculation (R Square/Determination Coefficient) or the influence of ROHIS activities on PAI learning outcomes is R2 x 100% = 0.4422 x 100% = 19.5%. This means that the contribution of ROHIS activities affects PAI learning outcomes by 19.5%, while 80.5% is influenced by other factors. These factors may include external and internal factors.
References
Y. Zhang, W. He, H. Lu, and H. Ji, “Mode Analysis on Biopharmaceutical Engineering Undergraduate Education in China Based on SPSS: SPSS Analysis on Biopharmaceutical Engineering Undergraduate Education in China,” in Proceedings - 2021 International Conference on Education, Information Management and Service Science, EIMSS 2021, School of Biology and Food Engineering, Changshu Institute of Technology, Changshu, China: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2021, pp. 128–135. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/EIMSS53851.2021.00036.
X. Zheng and F. Xie, “The influence of maker education on the innovation ability of secondary vocational students Based on Experimental Analysis of SPSS,” in Proceedings - 2021 2nd International Conference on Information Science and Education, ICISE-IE 2021, School of Information Science and Engineering, Shandong Normal University, Shandong, Jinan, China: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2021, pp. 1494–1498. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICISE-IE53922.2021.00333.
L. Yanghui, “Discussion on Disaster Education and Prevention Strategies Based on SPSS Analysis - Taking disaster prevention research of Chengdu as an example,” in E3S Web of Conferences, I. M.S. and L. W., Eds., Institute for Disaster Management and Reconstruction, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065, China: EDP Sciences, 2021. doi: https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202129203033.
F. Flores Ccanto et al., “Case Study Module with SPSS for the Learning of Statistics Seminar Applied to Educational Research in Doctoral Students of the National University of Education Enrique Guzmán y Valle,” in Proceedings - 2020 3rd International Conference of Inclusive Technology and Education, CONTIE 2020, Enrique Guzmán y Valle National University of Education, Lima, Peru: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2020, pp. 196–201. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CONTIE51334.2020.00043.
H. Zhao, “Research on Teaching Reform of English for Non-majors in Chinese Higher Vocational Education from the Perspective of Needs Analysis on EOP Based on SPSS Software,” in Proceedings - 2021 2nd International Conference on Big Data and Informatization Education, ICBDIE 2021, Shandong Transport Vocational College, Department of Science and Humanities, Shandong Province, Weifang, China: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2021, pp. 509–513. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICBDIE52740.2021.00122.
F. Zhang and W. Zhang, “Challenges and Countermeasures of the Ideological and Political Education for Social Enrollment in Higher Vocational Colleges Based on SPSS Analysis,” in Proceedings - 2021 2nd International Conference on Information Science and Education, ICISE-IE 2021, Foshan Polytechnic, Guangdong, Foshan, China: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2021, pp. 349–352. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICISE-IE53922.2021.00087.
J. Yang and Y. Zhang, “RETRACTED: Research on the factors affecting consumer trust in green residences—Based on SEM model and SPSS data processing software, (International Journal of Electrical Engineering & Education, (2020)),” Int. J. Electr. Eng. Educ., vol. 60, no. 1_suppl, pp. 885–898, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0020720920930351.
Y. Chen, “An empirical analysis of the flipped classroom about information literacy education in Chinese university based on SPSS 19.0,” in Proceedings - 2021 2nd International Conference on Information Science and Education, ICISE-IE 2021, Guangdong University of Finance and Economics, Guangdong, Guangzhou, China: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2021, pp. 67–70. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICISE-IE53922.2021.00023.
Y. Wang and W. Tong, “Analysis of China’s education informatization in the post-epidemic era based on SPSS Chi-square test and SWOT model,” in Proceedings - 2021 2nd International Conference on Information Science and Education, ICISE-IE 2021, College of Applied Science and Technology, Hainan University, Hainan Province, Danzhou, China: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2021, pp. 644–647. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICISE-IE53922.2021.00151.
L. Yin, H. Hassan, and M. Mokhtar, “Application of SPSS Data Processing Technology in International Education in China,” in Proceedings - 2021 2nd International Conference on Education, Knowledge and Information Management, ICEKIM 2021, Faculty of Social Sciences and Humanities, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Johor Bahru, Malaysia: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2021, pp. 570–573. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEKIM52309.2021.00130.
W. Widodo, “Kalaborasi Pendidikan Formal dan Boarding School,” J. Pedagog., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 1–7, 2018.
W. Widodo, “Objek Kajian dan Urgensi Mempelajari Sejarah dan Peradaban Islam,” J. Pedagog., vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 7–11, 2017.
R. Murtyaningsih, “Kontribusi Etos Kerja Islami Terhadap Kinerja Dosen,” J. Pedagog., vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 139–156, 2021.
R. Murtyaningsih, “Peranan Guru dalam Memotivasi Belajar Siswa,” J. Pedagog., vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 38–48, 2019.
A. Nurhartanto, “Penerapan Pembelajaran Metode One Day One Ayat Dalam Menghafal Juz’Amma Di TK Muslimat VI Andongrejo Kec. Banjarejo Kab. Blora Tahun Pelajaran 2021/2022,” J. Pedagog., vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 164–176, 2022.
W. Widodo, “Mengkritisi Faktor-Faktor Kegagalan Akademik Siswa dalam Belajar,” J. Pedagog., vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 110–125, 2019.
W. Widodo, “Konsep Ikhlas Dalam Novel Hafalan Shalat Delisa Karya Tereliye,” J. Pedagog., vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 6–19, 2019.
R. Murtyaningsih, “Manajemen Kurikulum Pendidikan Islam Di Masa Pandemi,” J. Pedagog., vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 99–110, 2021.
R. Murtyaningsih, “Pengaruh Pemberian Hukuman terhadap Kedisiplinan Siswa SMK Muhammadiyah 2 Blora Kelas XI TSM 4 Tahun Pelajaran 2016/2017,” J. Pedagog., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 38–46, 2018.
R. Murtyaningsih, “Transformasi dan Inovasi Manajemen Pendidikan Islam,” J. Pedagog., vol. 12, no. 2 SE-Articles, pp. 61–77, Dec. 2019, [Online]. Available: https://jurnal.staimuhblora.ac.id/index.php/pedagogy/article/view/6
A. Nurhartanto, “Metode Penafsiran Kontekstual Al-Qur’an Dalam Perspektif Ushul Fiqih: Kajian Terhadap Ayat-Ayat Keadilan,” J. Pedagog., vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 93–102, 2023.
R. Murtyaningsih, “Manajemen Strategi Dalam Meningkatkan Mutu Pendidikan Di Program Studi Pendidikan Agama Islam STAIM Blora,” J. Pedagog., vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 51–66, 2022.
A. Nurhartanto, “Ushul Fiqih Dan Fungsinya Dalm Kajian Hukum Islam,” J. Pedagog., vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 39–51, 2021.
A. Nurhartanto, “Shalat dan Pengaruhnya Dalam Membentuk Akhlakul Karimah (Suatu Tinjauan Kependidikan),” J. Pedagog., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 47–59, 2018.
R. Murtyaningsih, “Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia Dalam Praktik Peningkatan Mutu Pendidikan Di STAI Muhammadiyah Blora,” J. Pedagog., vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 52–74, 2022.
A. Nurhartanto, “Upaya Meningkatkan Nilai-Nilai Moderasi Beragama Di STAI Muhammadiyah Blora Melalui Penguatan Pemahaman Kaidah Kaidah Ushul Fiqih,” J. Pedagog., vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 88–101, 2022.
R. Murtyaningsih, “Perbandingan Kurikulum Berbasis Kompetensi (KBK) dengan Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP),” J. Pedagog., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 26–36, 2017.
R. Murtyaningsih, “Implementasi Metode Pembelajaran Everyone is a Teacher Here untuk Meningkatkan Prestasi Belajar Pendidikan Agama Islam di SMK Muhammadiyah 2 Blora,” J. Pedagog., vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 140–159, 2017.
A. Nurhartanto, “Metode Penafsiran Dalam Ushul Fiqih Kontemporer: Kajian Terhadap Pendekatan Literal Dan Kontekstual,” J. Pedagog., vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 55–66, 2023.
P. Roszak, S. Horvat, and J. Wółkowski, “Microaggressions and discriminatory behaviour towards religious education teachers in polish schools,” Br. J. Relig. Educ., vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 337–348, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01416200.2020.1832044.
M. J. Adon, “The Spirituality of Catholic Teachers in Implementing Multicultural Education in Indonesia,” Millah J. Relig. Stud., vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 275–310, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.20885/millah.vol21.iss1.art10.
Z. Abidin, “The Strategy of Islamic Religious Teachers in the Development of Akhlakul Karimah in Integrated Islamic Elementary School Students,” Munaddhomah, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 425–432, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.31538/munaddhomah.v3i4.437.
S. Erduran, L. Guilfoyle, and W. Park, “Science and Religious Education Teachers’ Views of Argumentation and Its Teaching,” Res. Sci. Educ., vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 655–673, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11165-020-09966-2.
H. C. A. Kistoro, S. Ru’iya, D. Husna, and N. M. Burhan, “Dynamics of the Implementation of Experience-Based Religious Learning in Indonesian and Malaysian Senior High Schools,” J. Pendidik. Agama Islam, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 283–296, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.14421/jpai.2022.192-08.
N. Lindström and L. Samuelsson, “On how re teachers address the sometimes conflicting tasks of conveying fundamental values and facilitating critical thinking,” Athens J. Educ., vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 23–36, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.30958/AJE.9-1-2.
L. G. Otaya, H. Anwar, and K. Yahiji, “The Assessment of Fit Data Model Feasibility of the Teachers’ Pedagogic Competency Variables,” Int. J. Instr., vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 909–926, 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2023.16248a.
J. Flood, D. Lapp, J. R. Squire, and J. M. Jensen, Methods of research on teaching the English language arts: The methodology chapters from the Handbook of research on teaching the English language arts: Sponsored by International Reading Association & National Council of Teachers of English: Second editi. San Diego State University, United States: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2004. doi: https://doi.org/10.4324/9781410612083.
D. Crowther and L. M. Lauesen, “Qualitative methods,” in Handbook of Research Methods in Corporate Social Responsibility, Leicester Business School, De Montfort University, United Kingdom: Edward Elgar Publishing Ltd., 2017, pp. 225–229. [Online]. Available: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85087675119&partnerID=40&md5=def177a5912950a3588f710fbb9d4273
UU RI No. 20, “Undang-undang (UU) Nomor 20 Tahun 2003 tentang Sistem Pendidikan Nasional,” 8 Juli 2003, Jakarta, Jul. 08, 2003.
A. Nillia, “Perbedaan Ilmu Pendidikan Islam dengan Ilmu Pendidikan Agama Islam,” KOMPASIANA. [Online]. Available: https://www.kompasiana.com/niliaadilla/6506fb516e14f16daf621f12/perbedaan-ilmu-pendidikan-islam-dengan-ilmu-pendidikan-agama-islam
K. Putra, “Pendidikan adalah Ibu dari Ilmu Pengetahuan,” tatkala.co.
Z. Daradjat, Ilmu Jiwa Agama. Jakarta: Bulan Bintang, 2003.
Z. Daradjat, Ilmu Pendidikan Islam. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara, 2011.
H. Aulia, “Mengatasi Rendahnya Hasil Belajar Siswa pada Pelajaran Agama Islam: Penyebab dan Solusinya Halaman 1 - Kompasiana.com.” Accessed: Apr. 02, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.kompasiana.com/hizbulaulia8394/652739e2edff7663d2310cc2/mengatasi-rendahnya-hasil-belajar-siswa-pada-pelajaran-agama-islam-penyebab-dan-solusinya
A. Rahman, “Paradigma baru pembelajaran PAI telaah keberhasilan model dsl (dakwah sistem langsung) di SMK Negeri 8 Jakarta,” Oct. 2010, [Online]. Available: https://repository.uinjkt.ac.id/dspace/handle/123456789/6251
B. Suryosubroto;, Proses Belajar Mengajar Di Sekolah. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta, 2002.
E. Komala and W. Unang, “Pengaruh Pembinaan Kerohanian Islam Terhadap Prestasi Belajar Pendidikan Agama Islam dan Budi Pekerti Siswa.” [Online]. Available: https://jurnal.staialhidayahbogor.ac.id/index.php/cendikia/article/view/2756/1155
https://kbbi.web.id/keagamaan, “Arti kata keagamaan - Kamus Besar Bahasa Indonesia (KBBI) Online.” Accessed: Aug. 22, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://kbbi.web.id/keagamaan
N. Nurdin, Pedoman pembinaan ROHIS di sekolah dan madrasah. Jakarta: Emir, 2018.
H. M. Arifin, Ilmu Pendidikan Islam. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara, 2003.
O. Hamalik, Psikologi belajar dan mengajar : Membantu guru dalam perencanaan pengajaran, penilaian perilaku, dan memberi kemudahan kepada siswa dalam belajar. Bandung: Sinar Baru Algensindo, 2014.
S. Slameto, Belajar dan Faktor-faktor yang Mempengaruhinya, Revisi. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta, 2015.
S. Arikunto, Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan Praktik. Rineka Cipta, 2009.
V. Herlina, “Elex Media Komputindo,” Elex Media Komputindo. Accessed: Apr. 02, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://elexmedia.id/
S. Sugiyono, Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif, Kualitatif, dan R&D. Bandung: Alphabeta, 2019.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Eva Siti Faridah, Salma Aisyah Amini (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



















